Mo
Ni
ANOMALOUS EFFECTS OF SCATTERING BY AGING CRYSTALS AND SOLID SOLUTIONS
Barabash R.I.
National Technical University of Ukraine, pr. Pobedy 37, Kiev 56, Ukraine
Keywords: X-ray , Neutron Scattering, Aging,
Cluster, Precipitates, Impurities, Intensity
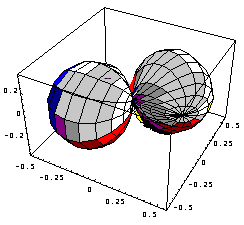
In solid solutions at small concentrations of impurities the overlapping of strongly distorted regions around impurity atoms and their correlation can be neglected. In that case different defects scatter independently and give an additive input into diffuse scattering intensity I1. Then total diffuse scattering may be presented as a sum of Huang scattering intensity IH and asymmetric part of scattering intensity Ia: I1= IH+ Ia. In the vicinity of reciprocal lattice points (when deviation vector q between the exact position of reciprocal lattice vector G and diffraction vector Q is small) diffuse scattering is influenced mainly by static distortions at large distances from the impurity. Then asymmetric part depending on the change of structure amplitudes is also small and total diffuse scattering coincides with classic Huang scattering IH. The shape of the surface of equal intensity (isodiffuse surface) around reciprocal lattice point depends on the symmetry of displacement field caused by impurity atom. For cubic defects in cubic crystals it is always double drop being proportional IH(Qq)2/q2 . For noncubic defects it may change to concave or single drop. Elastic anisotropy (x) of the crystal can slightly change the shape of isodiffuse surface but the type of the surface is retained . On the Fig.1a,b there are shown isodiffuse surfaces around (110) reflection for scattering by point defects in bcc Mo (x=0.58) and fcc Ni (x=-1.2 ) crystals having opposite sign of elastic anisotropy. Cubic symmetry of defects in both cases results in the double drop shape of isodiffuse surface , and different sign of anisotropy creates some peculiarities on it.
Mo |
Ni |
 |
 |
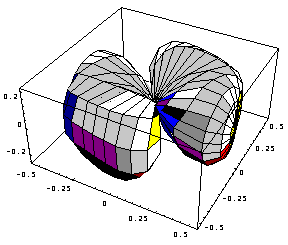
With the increase of impurities concentration the precipitation occurs. The presence of clusters causes larger local distortions due to the existence of lattice misfit between matrix and precipitate and the difference of structure amplitudes between precipitation and matrix. It causes the asymmetry of isodiffuse surfaces. The intensity becomes much higher at one side of reciprocal lattice point and the latter are not any longer the inversion centers for intensity distributions. Even the type of the surface may be changed due to the formation of clusters. If the cluster is surrounded by the layer where the impurity concentration level differs from that of matrix isodiffuse surfaces do not pass through reciprocal lattice points but surround them. The type of isodiffuse surfaces correlates with parameters of defects and their concentration.