STRUCTURE AND PHASE TRANSITION IN (C2H5NH3)4Sb3Cl13
Maciej Bujak,
Jacek Zaleski
Institute of Chemistry, University of Opole, ul. Oleska 48,
45-052 Opole, Poland
e-mail: mbujak@uni.opole.pl
Keywords: crystal structure, hydrogen bond,
phase transition.
Alkylammonium chloroantimonates are a new interesting family of compounds. They are defined by a general formula RaSbbClc (R-alkylammonium cation, a, b, c, stoichiometric coefficients, where c=3a+b). Those compounds attract recently growing attention since many salts of this group undergo numerous phase transitions, some of them to polar ferroelectric, ferrielectric or pyroelectric phases [1].
Those salts are obtained by mixing amine hydrochloride and antimony trichloride in organic solvent or water solution of hydrochloric acid. In the particular case of SbIII chlorides the following ions are usually obtained: SbCl41-, SbCl52-, SbCl63-, Sb2Cl93-[2,3]. They are ionic salts with anionic sublattices composed of deformed octahedra isolated (for larger in spatial dimensions cations) or connected with each other by corners, edges or faces. Alkylammonium cations located in anionic cavites are connected to anions by hydrogen bonds.
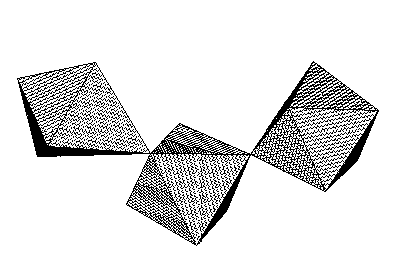
In present work we describe room temperature crystal structure of (C2H5NH3)4Sb3Cl13 (orthorhombic Pnma space group), a new member of the chloroantimonates family. Its anionic sublattice is composed of (Sb3Cl134-)n chains (Fig. 1) built of deformed SbCl63- octahedra connected by corners. Ethylammonium cations are connected to anions by weak N-H...Cl hydrogen bonds. The influence of hydrogen bonds on deformation of octahedral co-ordination of SbIII is dicussed.

(C2H5NH3)4Sb3Cl13
undergoes one structural phase transition below room temperature
at 270K. The investigation of phase transition by dieletric, DSC,
dilatometric and X-ray diffraction method is presented. The
mechanism of the transition is proposed.